
In order to reap the total mental, physical and psychological benefits of sleep, you need a comfortable place to rest that allows the brain to cycle through the 4 stages of sleep: NREM Stages 1, 2, and 3, and REM Sleep. NREM stands for Non-Rapid Eye Movement and characterizes the first three stages of sleep also known as “quiet sleep.” Stage 4 is REM sleep, also known as active sleep, dreaming sleep, or paradoxical sleep Trusted Source Paradoxical as a Sleep State and Disorder What is the definition of paradoxical sleep? Learn more about this REM sleep state and the word used as applied to insomnia and behavioral intention. www.verywellhealth.com . Getting to that fourth, called REM sleep is very important Trusted Source REM sleep: Definition, functions, the effects of alcohol, and disorde This article provides details on rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, why we need it, how to ensure we get it, and how REM sleep is affected by alcohol. We also explain how REM sleep ties in with our dreams plus how it relates to the other phases of sleep that are necessary to rest the body and restore the muscles. www.medicalnewstoday.com as that’s when our bodies and minds repair themselves. If we don’t complete the four stages of NREM to REM sleep cycle several times a night, then many health issues, including ones to do with fatigue, slow healing, migraines, depression, obesity, and memory, can be a consequence.
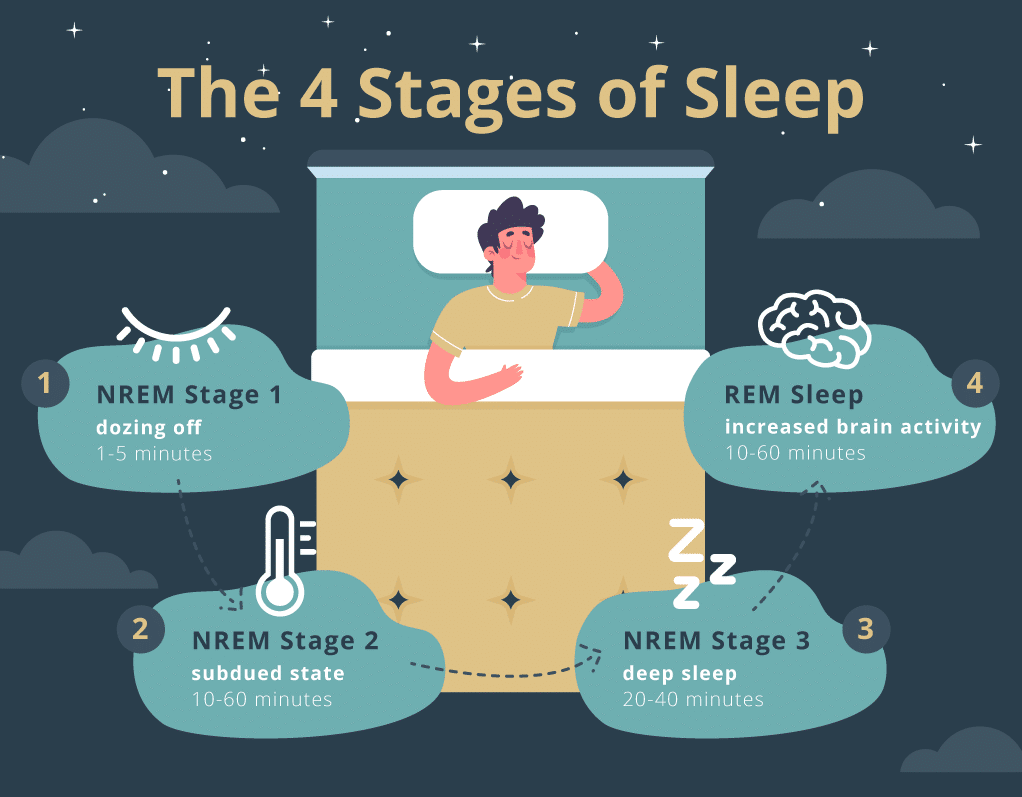
A sleep cycle consists of four main stages: NREM Stages 1, 2, and 3, and Stage 4, which is REM Sleep. NREM Stage 1 takes 1-5 minutes and happens when you are still slightly aware but feel yourself drifting. Stage 2 NREM takes 10 to 60 minutes and occurs when your heart and body temperature drop and your breathing becomes more regular as you become less conscious. Stage 3 NREM lasts between 20-40 minutes; you are completely relaxed, and your mind reviews the events of your conscious day. This progresses to the REM sleep that lasts between 10-60 minutes that helps you process information into memory and allows your body and mind to repair themselves. The full sleep cycle can last between 40 minutes to 165 minutes, and it must be experienced several times a night in order to maintain general health and wellness.
Sleep stages progress through 1 to 4, with the first 3 stages being NREM and stage 4 being REM. Sometimes this is referred to as the 5 stages of sleep because, after stage 3, the body repeats stage 2, before entering stage 3 again.
| Sleep Stages | Type of Sleep | Other Names | Duration |
| Stage 1 | NREM | N1 | 1-5 minutes |
| Stage 2 | NREM | N2 | 10-60 minutes |
| Stage 3 | NREM | N3, Slow-Wave Sleep (SWS), Delta Sleep, Deep Sleep | 20-40 minutes |
| Stage 4 | REM | REM Sleep | 10-60 minutes |
An NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) is a lighter sleep stage where there is no experience of rapid eye movement. During the first three stages of sleep, the brain produces beta waves, that on an electroencephalogram (EEG Trusted Source EEG (electroencephalogram) - Mayo Clinic An EEG is one of the main diagnostic tests for epilepsy. www.mayoclinic.org ), a machine that measures brain activity, shows short spikes on a paper graph when recorded. The first 3 stages of a full sleep cycle are lighter NREM stages.
During stage 1 the person is still aware and gravitates from being awake or entering a very light sleep. NREM Stage 1 takes 1-5 minutes to complete.
During stage 2, body temperature and heart rate slow down. Breathing becomes rhythmic. The person enters a slightly deeper state that lasts between 10 and 60 minutes.
The person enters slow-wave sleep, also known as delta sleep, for 20-40 minutes. The muscles relax, blood nourishes tissues, and hormones help to repair itself.
After NREM Stage 3 the body returns to being in lighter sleep, returning to a lowering of the heart rate, for 10 to 60 minutes.
During the REM sleep stage of Rapid Eye Movement occurs for 10-60 minutes. Your brain and body experience:
Elderly individuals may experience atonia during REM sleep. This is a protective state of temporary paralysis that prevents the person from hurting themselves while acting out their dreams.
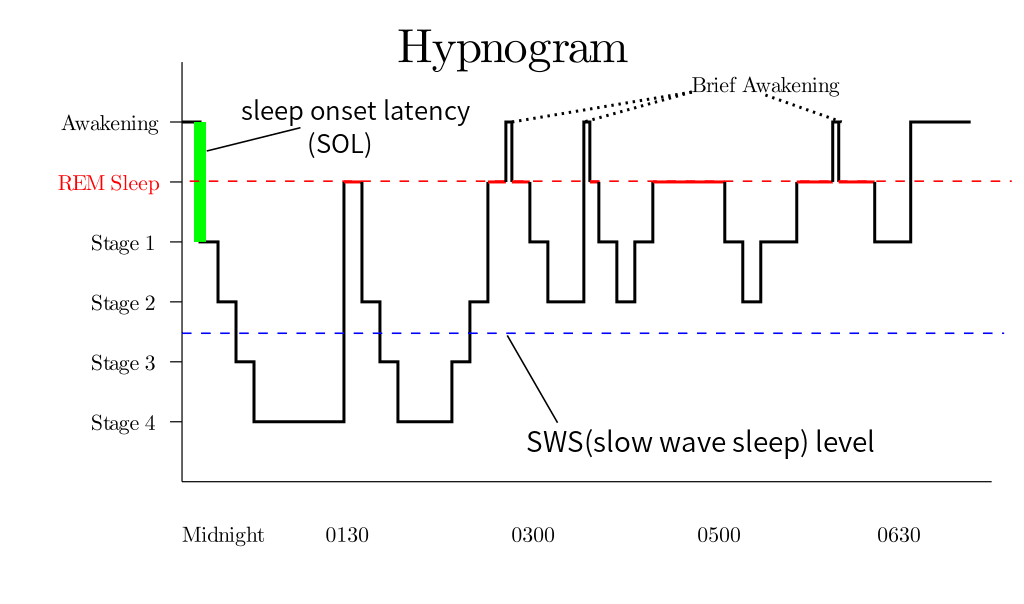
REM Stage R is another name for the REM sleep cycle that starts about 90 minutes after you first fall asleep for most people. Stage R sleep cycles back to 3 and back again for several cycles with REM lasting about ten minutes and then progressively lengthening to an hour with each re-entry. It is sometimes called paradoxical sleep because although you are in the deepest sleep possible, your brain is actively alert as if you were completely awake.
Completing a full sleep stage sequence several times a night is crucial to well-being. It is important to keep cycling back to the REM stage as that is when your body replenishes itself. If you are stalled in stage one or two due to a medical condition, medication side-effects, secondhand smoke or noise, or do not stay in the REM sleep stage long enough (from 10 minutes to an hour), then your overall health can degrade in the following ways:
The result is often more sleep deprivation.
If you are not cycling through all the stages of sleep, then you are suffering from sleep deprivation Trusted Source Sleep Deprivation and Migraines | Sleep Foundation How are sleep deprivation and migraines connected? Learn how a lack of sleep may be causing your headaches with our in-depth guide. www.sleepfoundation.org . This is usually due to reduced opportunities to rest. There are many reasons for these reduced sleep opportunities, including lifestyle, sleeping habits, age, mental health, health issues, insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, narcolepsy, and shift work.
Lifestyle changes can be made to provide you with that full 8 hours of sleep needed to experience all of the sleep stages several times a night. One of the most important is the reduction or complete cessation of recreational drug use, alcohol consumption, and tobacco, all of which overstimulate the brain and cause respiratory issues. Overexposure to cellphones, computers, and especially social media has also been known to affect sleeping patterns.
Many people have chronic behaviors that may be sabotaging their current sleep cycles without them even knowing it. Changing your sleeping pattern by going to bed by 11 am and getting up by 7 am is recommended by many health and wellness experts to get that full 8 hours of sleep that will allow you to get the several sleep cycles needed for mental and physical repair.
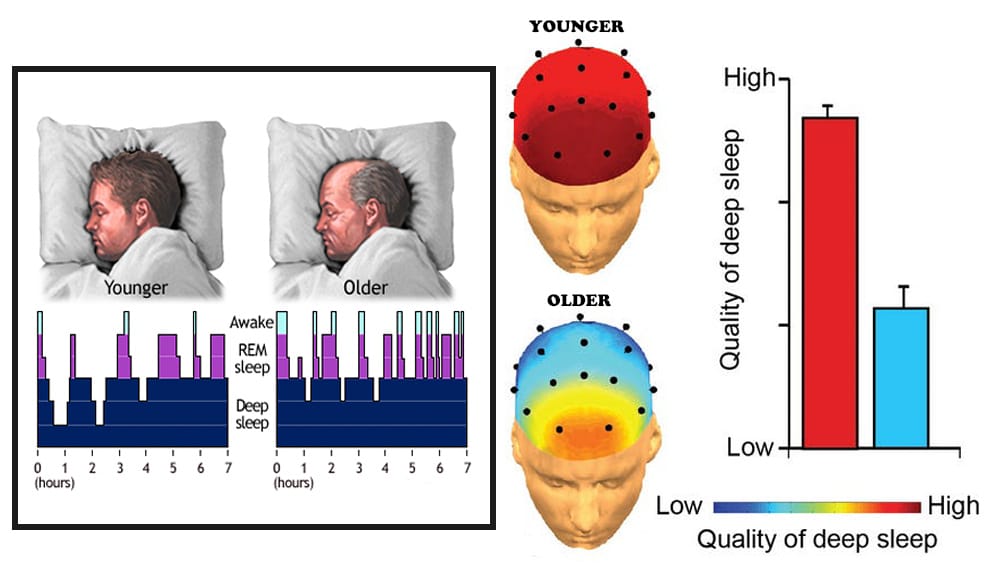
The elderly tend to wake up more during the night as well as wake up earlier, rarely sleeping more than 6 hours a night.
Mental health issues such as anxiety, post-stress-traumatic-disorder, and bipolar disorder can cause sleeplessness, as can the medications used to treat them. Insomnia associated with grief, hyper-vigilance, and borderline personality disorders can also disrupt sleep.
Almost any health issue can disrupt a good night’s sleep, and this includes everything from the stomach flu to dental pain to a brain tumor. It is important to make yourself as comfortable as possible, especially if you have strained or broken bones.
Suppose you are in pain because of rheumatism, a hip operation, diabetic neuropathy, or another issue. In that case, you might want to consider getting an adjustable bed frame to relieve any pressure on points such as the neck, hips, and lower back and any swelling in the legs or feet. Sweet Night makes a light bed frame that raises at both the head and the foot of the bed so that you can be as comfortable as possible at night.
Insomnia is a complex disorder that varies from person to person and can be acute (short-term) due to grief or an illness or chronic (long-term) due to chemical brain imbalances, stress, or trauma. Medications and recreational drug use can also cause insomnia.
Sleep apnea is a condition where the airways to the lung are either blocked or neurologically affected in a way that causes the person to stop breathing during the night. This disrupts the sleep cycle, often rebooting the person back to sleep stage 1 or 2 when they should sleep stage 4.
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder that causes your legs to move or twitch whenever you are at rest. The aching, creeping, and pulling sensations associated with this disorder waking you up and interrupt the four-stage sleep cycle.
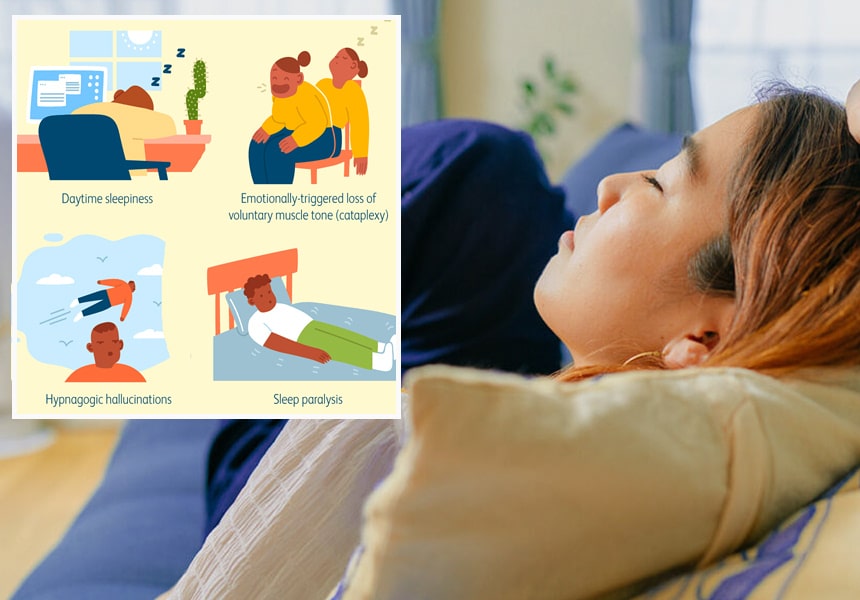

Narcolepsy is a state that may or may not be caused by interrupted sleep cycles, where the immune system attacks the brain and causes a chemical balance. The result is a constantly dozing individual that seems to sleepwalk, sometimes in a dream state all day.
Being a shift worker is one of the main culprits for sleeplessness, causing people to stay up for too many hours in a row or to be working when they are sleeping, thus disrupting the body’s clock.
Here are some measures you can take to get a more restful sleep.
Now that you know all about the order of sleep stages, the stages of sleep and brain waves, and the stages of sleep deprivation. It is your breathing and overall tendency to suddenly wake up at night, for whatever reason that mostly regulates how many times you are going to be able to complete the 4 stages of sleep and arrive at the all-important REM vivid dreaming stage, so address any conditions that affect that. You have good advice about taking control of the situation and any mental or physical health consequences that might be the result of not getting enough shut-eye at night. It is easy to take charge of your health by improving your sleeping environment by keeping it dark, airy, and cool, avoiding eating, exercise, and stimulation at night, and buying a great mattress or adjustable bed that promotes pain relief, peace, and uninterrupted sleep cycles.





